Mallory Vincent, MBA •
With more time at home during the COVID 19 pandemic, now may be the time to start that degree you have always wanted to earn. Not only will you have fewer distractions due to your practically non-existent social life, but you could also get a tax credit or income adjustment on your 2020 tax return. Education credits are amounts that will reduce the amount of tax due of your tax return. They are based on qualified education expenses that you paid during the year including tuition and certain related expenses.
With more time at home during the COVID 19 pandemic, now may be the time to start that degree you have always wanted to earn. Not only will you have fewer distractions due to your practically non-existent social life, but you could also get a tax credit or income adjustment on your 2020 tax return. Education credits are amounts that will reduce the amount of tax due of your tax return. They are based on qualified education expenses that you paid during the year including tuition and certain related expenses.
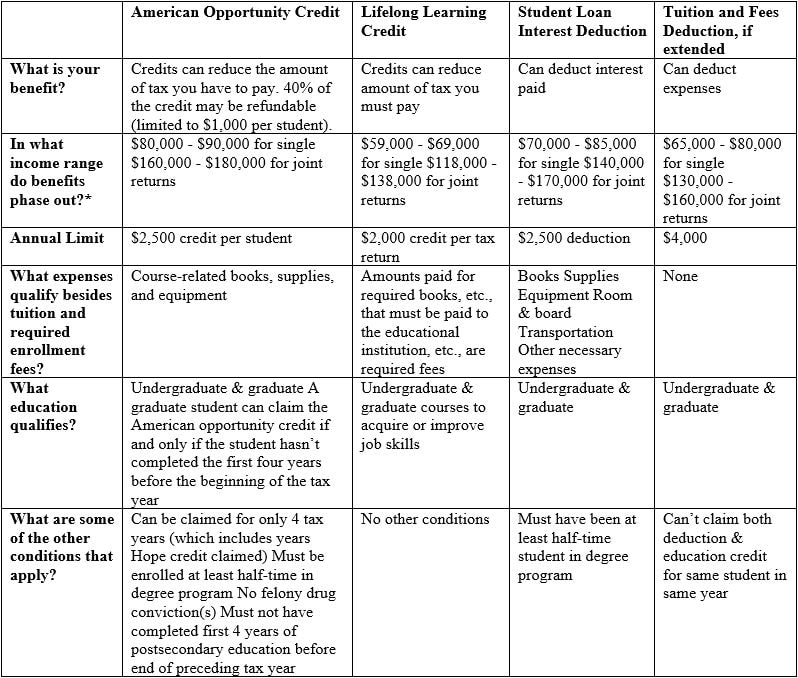
There are different types of education benefits available, including the American opportunity credit, lifetime learning credit, and the tuition and fees deduction. Note that these are limited based on your modified adjusted gross income (MAGI) and you will not receive any benefit if your MAGI is over the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) thresholds as your benefit would be completely reduced, or phased out (see tax year 2020 limits in the table below).
Your school will provide you with a Form 1098-T, Tuition Statement, for the tax year. It will include any qualified education expenses paid and scholarships earned (which offset the total qualified education expenses) throughout the year. You can add in other expenses that qualify for education credits such as books or supplies not purchased through your school account. Unfortunately, expenses such as room and board, insurance, medical expenses (including student health fees), transportation costs, or other personal, living, or family expenses, do not qualify towards the credit.
Let’s face it - earning a degree is expensive. Another benefit available is that if you take out a qualified student loan to pay for qualified education expenses, the amount of student loan interest you pay can be deducted up to $2,500 annually. This is a direct adjustment to your income as long as your tax return filing status is not married filing separately. You will receive a Form 1098-E, Student Loan Interest Statement, or another statement from the lender showing the amount of interest paid during the year. For more information on whether or not these tax benefits could apply to you, read IRS Publication 970 and Education Credits: Questions and Answers on the IRS website. The below table summarizes some of the most common education tax benefits:
Your school will provide you with a Form 1098-T, Tuition Statement, for the tax year. It will include any qualified education expenses paid and scholarships earned (which offset the total qualified education expenses) throughout the year. You can add in other expenses that qualify for education credits such as books or supplies not purchased through your school account. Unfortunately, expenses such as room and board, insurance, medical expenses (including student health fees), transportation costs, or other personal, living, or family expenses, do not qualify towards the credit.
Let’s face it - earning a degree is expensive. Another benefit available is that if you take out a qualified student loan to pay for qualified education expenses, the amount of student loan interest you pay can be deducted up to $2,500 annually. This is a direct adjustment to your income as long as your tax return filing status is not married filing separately. You will receive a Form 1098-E, Student Loan Interest Statement, or another statement from the lender showing the amount of interest paid during the year. For more information on whether or not these tax benefits could apply to you, read IRS Publication 970 and Education Credits: Questions and Answers on the IRS website. The below table summarizes some of the most common education tax benefits:
*MAGI phase-out amounts include IRS tax inflation adjustments for tax year 2020.
Even if you qualify for one or more of the above tax breaks, you cannot claim the American opportunity credit and the tuition and fees deduction for the same expenses, and you cannot claim an education credit using expenses paid for with a 529 Plan; therefore, make sure to contact your tax professional to coordinate education benefits and maximize your refund. In addition, be sure to keep accurate records for any qualified education expenses you use to claim education credits and deductions.
Even if you qualify for one or more of the above tax breaks, you cannot claim the American opportunity credit and the tuition and fees deduction for the same expenses, and you cannot claim an education credit using expenses paid for with a 529 Plan; therefore, make sure to contact your tax professional to coordinate education benefits and maximize your refund. In addition, be sure to keep accurate records for any qualified education expenses you use to claim education credits and deductions.

 RSS Feed
RSS Feed